
Our Most Common Service
Are you in need of a dependable tax return service?
Our firm specializes in tax return services tailored for U.S. Expats living in Japan. We cover everything from federal and state tax return preparation to a range of other tax-related tasks.
Tax returns for U.S. Expats in Japan involve a higher level of complexity due to international tax compliance.
For instance, if you have income from rental properties or securities accounts in Japan, the income tax incurred in Japan becomes a Foreign Tax Credit on your U.S. tax return. It is crucial to accurately reflect the calculation and carryover amount of the Foreign Tax Credit in your tax filing.
Failing to accurately reflect this in the tax return process can result in the income being subject to taxation in both Japan and the U.S. (double taxation), which can be a significant burden for the U.S. Expats.
Furthermore, international tax compliance involves the obligation of Informational Returns. One prominent example of an Informational Return is the FBAR reporting, which requires disclosure of Japanese bank and financial accounts.
Failing to understand the obligation of Informational Returns may lead to potential claims for additional taxes and penalties from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and in some cases, may even lead to multiple tax audits.
We are well-versed in various Japanese tax returns and Japanese income documents. This enables us to effectively avoid double taxation, adhere to informational return requirements, and provide you with a bilingual (English and Japanese) service you can trust and rely on.
Contents
Federal Income Tax Return

U.S. Expats are considered U.S. residents and thus have an obligation to file federal tax returns every year.
For U.S. Expats, the scope of income subject to taxation in Federal income tax return becomes worldwide income. Therefore, even if you reside in Japan, you are required to file Federal income tax return and include income earned in Japan.
The deadline for filing the federal tax return is typically April 15th. If you’re unable to gather your tax information before the deadline, you will need to apply for a six-month extension.
Before applying for an extension, if you anticipate that there will be a tax liability based on an estimated calculation, it is necessary to make a payment for the estimated tax along with the extension request.
Failing to estimate and only applying for an extension, then subsequently finding out there is a tax liability when filing the actual return, may result in penalties and interest for the amount due.
For U.S. Expats using our Federal income tax service, we offer a complimentary service for providing estimates of both extension requests and estimated tax payments.
State Income Tax Return
Another crucial aspect to consider in U.S. tax filing is state income tax.
Expats who reside in Japan and have rental properties or trust distributions at the state with an income tax, you must file for state tax returns. In some states, there may also be a requirement to file local (county or city) tax returns.
Furthermore, due to variations in state tax laws, it’s important to be aware of different aspects such as states where foreign tax credits are applicable and states that follow the U.S.-Japan Tax Treaty.
Our firm provides services for preparing state tax returns for all states with an income tax. We stay up-to-date with the rapidly changing state tax laws and can navigate compliance across multiple states.
- Nevada
- Alaska
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Florida
- South Dakota
- Wyoming
The deadline for filing state tax returns is typically April 15th, the same as the federal deadline. If you’re unable to gather your tax information before the deadline, you will need to apply for a six-month extension, just as with federal taxes.
In some states, they automatically grant a six-month extension even if you don’t apply for one. For example, in Hawaii personal income tax, they automatically allow a six-month extension for filing tax returns. However, one condition for this automatic extension is that you must make an estimated tax payment by the extension deadline. If you fail to make this payment, they will not grant the automatic extension, and you will have to pay the tax amount along with any penalties for late payment.
Therefore, when applying for a state extension, it is crucial to estimate the expected tax liability and proceed with the payment before the extension deadline.
For U.S. Expats using our state tax filing service, we offer a complimentary service for providing assistance with state extension requests and estimates for tax payments.
FBAR Filing

The FBAR (Foreign Bank Account Report) and FATCA (Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act) filings are informational returns where individuals disclose financial accounts and assets held outside the United States. It is mandatory for eligible individuals to file FBAR and FATCA reports every year.
On August 16, 2022, President Biden signed the “Inflation Reduction Act,” which was subsequently enacted. This allocated approximately $80 billion to the IRS, and based on this budget, the IRS announced its operational plan on April 6, 2023.
According to the IRS’s operational plan, about 57% ($45 billion) of the budget is allocated to enforcement activities. This suggests an expected increase in IRS oversight and enforcement of FBAR and FATCA filings.
Our firm offers services for handling FBAR and FATCA filings. Additionally, we provide services for individuals who may not be aware of their FBAR and FATCA filing obligations, as well as services for amending FBAR filings for previous years.
Individuals subject to FBAR filing must meet both of the following conditions
- 1
U.S. citizen, Green card holder, U.S. tax resident, Dual-Status individuals
- 2
At any point during the calendar year, had a total of more than $10,000 in foreign financial accounts outside the United States.
The FBAR filing deadline aligns with the standard U.S. individual tax filing deadline, which is April 15th.
Regarding FBAR extension requests, an automatic extension of six months is granted. This automatic extension, referred to as the “Automatic Extension,” means that FBAR filers do not need to make a special request for an extension.
FATCA Filing
FATCA (Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act) is an informational return required by the IRS for U.S. Expats to disclose their foreign financial assets held outside the United States for tax purposes.
The form used for FATCA reporting is “Form 8938 – Statement of Specified Foreign Financial Assets.” In addition to reporting the balance of foreign financial assets held outside the United States, FATCA reporting also requires disclosure of taxable income generated from those financial assets, such as interest and capital gains.
Individuals subject to FATCA filing are those who meet one of the following two conditions:
- 1
U.S. citizen, Green card holder, U.S. tax resident, Dual-Status individuals
- 2
At any point during the year, they had a total of foreign financial assets exceeding the specified amounts below:
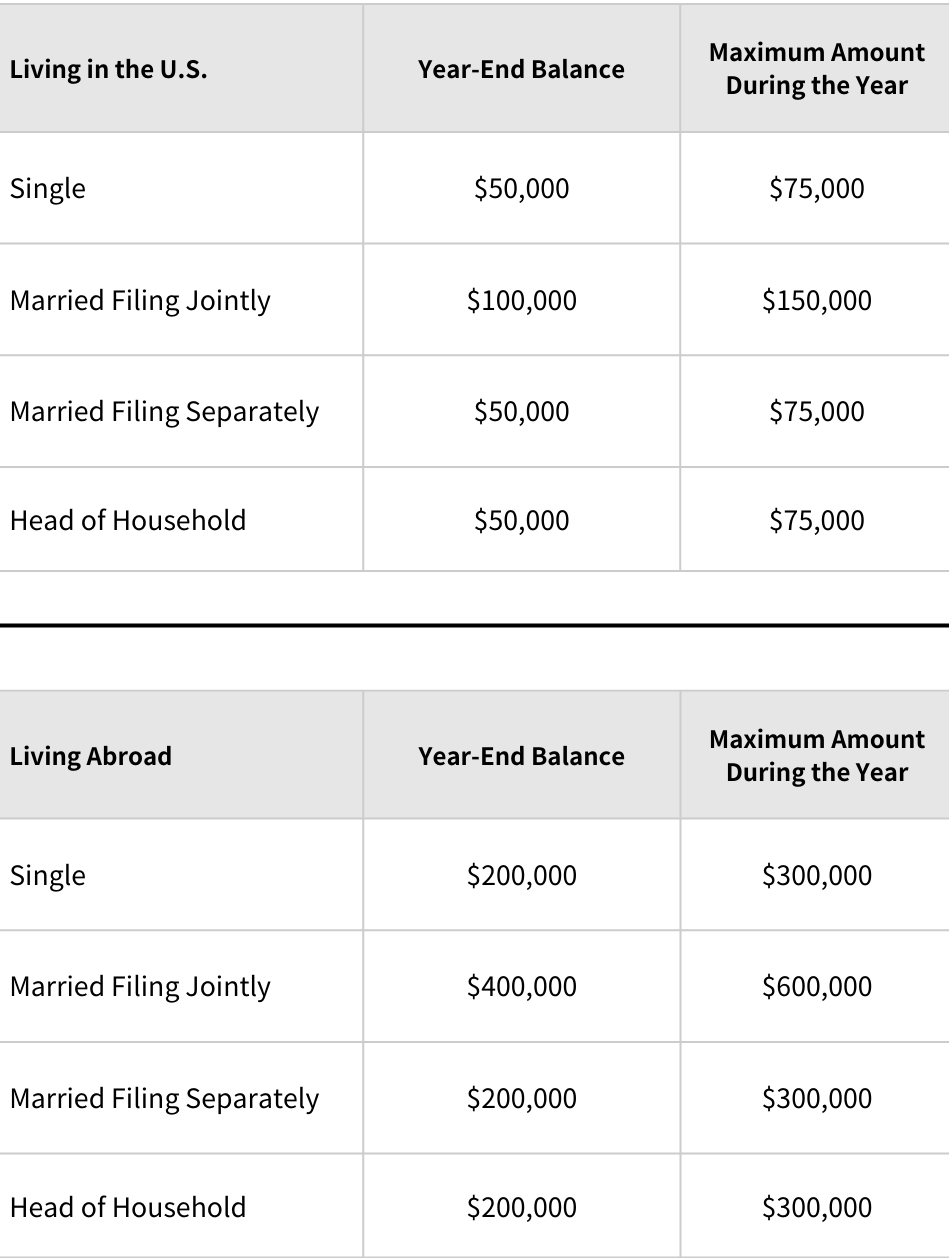
*“Living Abroad” refers to a “Bona Fide Resident” in that country. A “Bona Fide Resident” is someone who has lived in that country throughout the year or has resided in that country for 330 days or more in a 12-month period.
Many aspects of FATCA-eligible financial assets are similar to those for FBAR filing, but some additional foreign assets are included. The added financial assets are indicated in red.
The FATCA filing deadline aligns with the standard U.S. individual tax filing deadline, which is typically April 15th.
Regarding FATCA extension requests, by applying for an extension for your federal tax return, your FATCA filing deadline is also extended by six months.
The penalty for non-compliance with FATCA filing is $10,000 per year. Additionally, if there is no response to notifications from the IRS regarding FATCA non-compliance, penalties are added each month, with the maximum penalty reaching up to $50,000. Furthermore, for additional taxes resulting from unreported income generated by undisclosed foreign assets, a 40% penalty is applied.
Tax Consulting

In our tax consulting service, we provide tax notice assistance, we review the content of the tax notices you receive, provide translations of documents into Japanese, and arrange necessary paperwork.
We have a system in place that allows for efficient communication with the IRS, facilitated by our licensed Certified Public Accountant.


